File upload to Azure Blob Storage using Svelte Kit
table of contents
Working on the creation of recipes in cook-web I implemented the upload of their images to Azure Blob Storage.
The general diagram of the actual process in my application is as follows (I will use the numbers of each part for reference later):
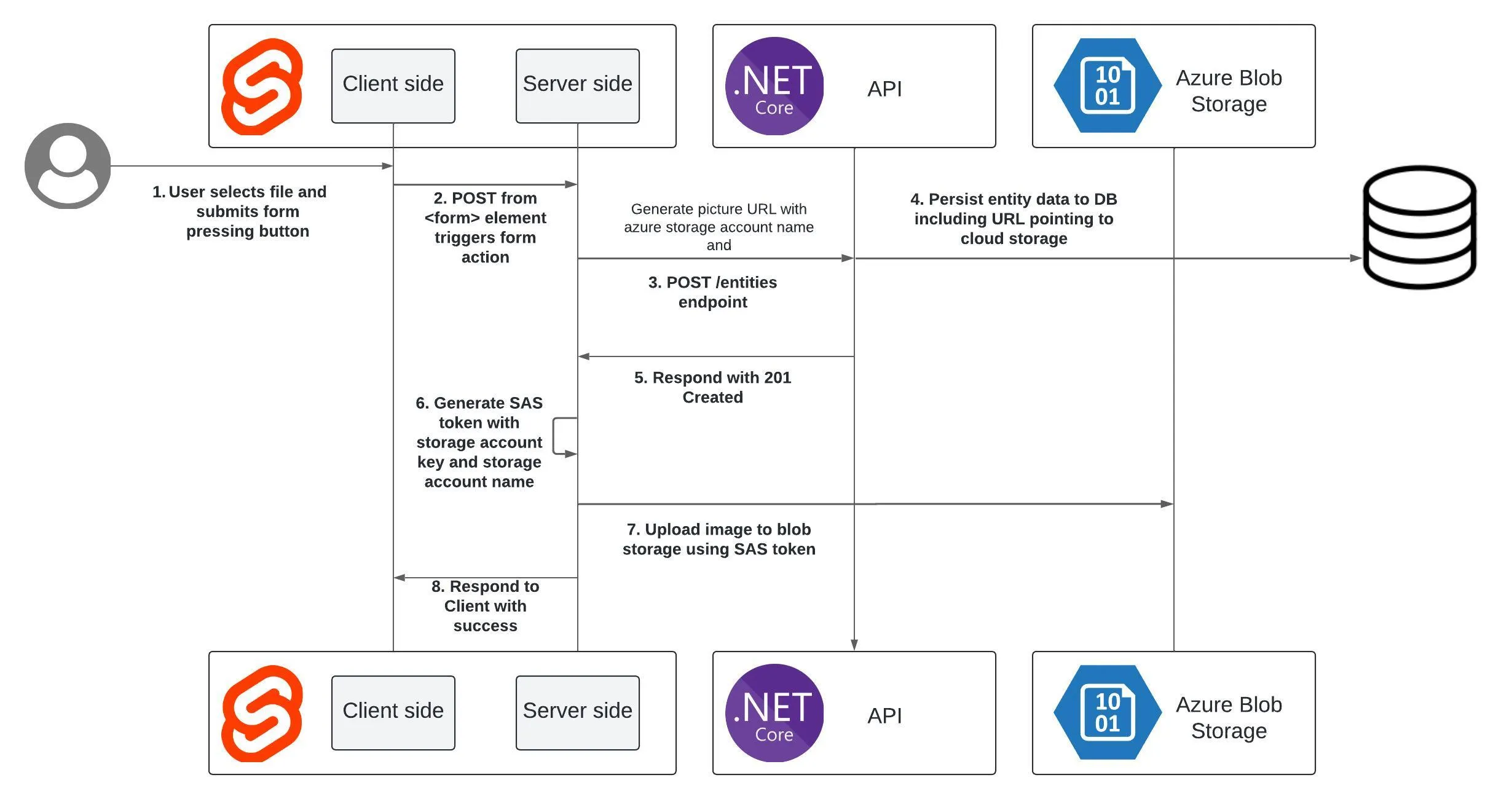
For illustrative purposes I am going to try to abstract as much as possible from the specifics of my particular case.
Versions:
- Svelte 4.2.7
- SvelteKit 2.0.0
- Vite 5.0.3
- Azure Storage Blob client library for JavaScript 12.17.0
- Typescript 5.0.0
1 SvelteKit client
The SvelteKit client side is relatively simple, in a page +page.svelte we place:
<script lang="ts">
let files: FileList | null;
let fileInput: HTMLInputElement;
</script>
<form method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<!-- Accept attribute value is an example, use whatever value you desire -->
<input
accept="image/png, image/jpg"
bind:files
id="myFile"
name="myFile"
type="file"
/>
<input
name="name"
type="text"
/>
<button type="submit">Subir archivo</button>
</form>
Something important to note is the value of the enctype attribute on the form element. It is necessary because if you use use:enhance as described in this issue. If not, when you press the submit button, this console error occurs and the POST action is not executed:
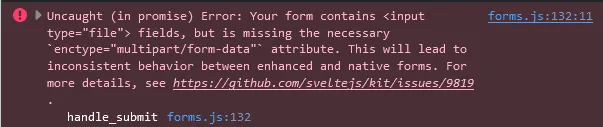
For ilustrative purposes I didn’t set use:enhance there but since I did in my repository I thought it was worth mentioning, took me a few minutes to open the console to figure out why nothing was happening when I was trying to submit the form.
2 - 4 SvelteKit Client -> SvelteKit Server
In the same path of +page.svelte we must have a +page.server.ts file that exports an action, which will be triggered when the form is submitted (docs). The file can export more than one action, besides the one exported by default (these additional are the named actions mentioned in the docs). In this case we only need the default one.
export const actions = {
default: async ({ request }) => {
const data = await request.formData();
const fileToUpload = data.get('myFile') as File;
// data.get('') returns a value of type FormDataEntryValue which
// it is a union of File and string so we can make an assert
// a File with the keyword as
const entityName = data.get('name');
// Creation of the entity through the API in the DB
const body = {
name: entityName,
files: [`https://${AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME}.blob.core.windows.net/${name}`]
};
const response = await fetch(`${env.API_URL}`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(body)
});
...
}
} satisfies Actions;
The file is obtained calling FormData.get. We then put together the request body to send to our API and use fetch to execute it.
The files property in the body of the request allows us, in a front end that consumes the API data, to know which URL corresponds to the entity’s image (a user, a post, a cooking recipe, etc.).
5-7 SvelteKit Server -> Azure Storage
Still in the default action of +page.server.ts, if the API response is successful (status code 201), we proceed with uploading the file to Azure:
...
if (response.status === 201) {
const responseJson = await response.json();
if (fileToUpload !== null) {
await uploadFile(fileToUpload, entityName);
}
return { success: true, data: responseJson };
}
return fail(response.status);
...
For the upload we will need two elements:
- A SAS shared access signature (a.k.a. SAS token): Provides delegated access to resources on a certain time window, with limited permissions, etc.
- The Azure storage account access key
Both elements should not be exposed to the client for security reasons and that is, in part, why we perform this process on SvelteKit server side.
For SAS shared access signing we first need to install the package @azure/storage-blob:
npm install @azure/storage-blob
With the following function we create the signature:
import {
generateAccountSASQueryParameters,
StorageSharedKeyCredential,
AccountSASServices,
AccountSASResourceTypes,
AccountSASPermissions,
SASProtocol,
BlobServiceClient
} from '@azure/storage-blob';
...
function createSasToken() {
const sasOptions = {
services: AccountSASServices.parse('b').toString(),
resourceTypes: AccountSASResourceTypes.parse('co').toString(),
permissions: AccountSASPermissions.parse('w'),
protocol: SASProtocol.Https,
expiresOn: new Date(new Date().valueOf() + 3 * 60 * 1000) // 3 minutos
};
const constants = {
accountName: env.AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME,
accountKey: env.AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_KEY
};
const sharedKeyCredential = new StorageSharedKeyCredential(
constants.accountName,
constants.accountKey
);
return generateAccountSASQueryParameters(sasOptions, sharedKeyCredential).toString();
}
In sasOptions we set the token properties:
- Permission to access containers and objects (‘bo’) of the Blob service (‘b’)
- Write permission (‘w’)
- Can only be access resources via HTTPS
- Expires after 3 minutes
Next to the name of the storage account and its key we can generate the signature with generateAccountSASQueryParameters. I used this material as a reference.
Finally, to use it when uploading the file we use the following function:
async function uploadFile(file: File, blobName: string) {
const sasToken = createSasToken();
const blobServiceClient = new BlobServiceClient(
`https://${env.AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME}.blob.core.windows.net?${sasToken}`
);
const containerClient = blobServiceClient.getContainerClient('ourContainerName');
const blockBlobClient = containerClient.getBlockBlobClient(blobName);
try {
await blockBlobClient.uploadData(Buffer.from(await file.arrayBuffer()));
} catch (error) {
console.error(`An error happened while trying to upload the file: ${error}`);
}
}
If you get a CORS error this link is helpful.
8 Response to user
Finally, the action in our +page.server.ts will have a form like the following:
export const actions = {
default: async ({ request }) => {
const data = await request.formData();
const fileToUpload = data.get('myFile') as File;
const entityName = data.get('name');
const body = {
name,
files: [`https://${AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME}.blob.core.windows.net/${name}`]
};
// POST /entidades y creación en la DB
const response = await fetch(`${env.API_URL}`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(body)
});
// 5 API responde con código de éxito 201
if (response.status === 201) {
const responseJson = await response.json();
if (file !== null) {
// 6 y 7 generación de token SAS y subida de archivo a Azure Blob Storage
await uploadFile(file, entityName);
}
// 8 Respuesta de éxito al cliente
return { success: true, data: responseJson };
}
return fail(response.status);
}
} satisfies Actions;
The uploadFile function can be included in the same file or another, depending on the organization of the project.
If you have any questions, feel free to reach me via e-mail (luzojeda@proton.me). In cook-web in src/routes/admin/crear-receta there is a specific example using all of the above but depending on the date there may already be differences about the concrete implementation.
References: